Organic gardening is more than just a trend—it’s a commitment to cultivating plants in a way that respects nature, promotes biodiversity, and produces healthier, chemical-free food. Whether you’re an experienced gardener or a beginner eager to grow your own vegetables and herbs, embracing organic methods can lead to a more sustainable and rewarding gardening experience. Here are essential tips to help you succeed in organic gardening.
1. Start with Healthy Soil
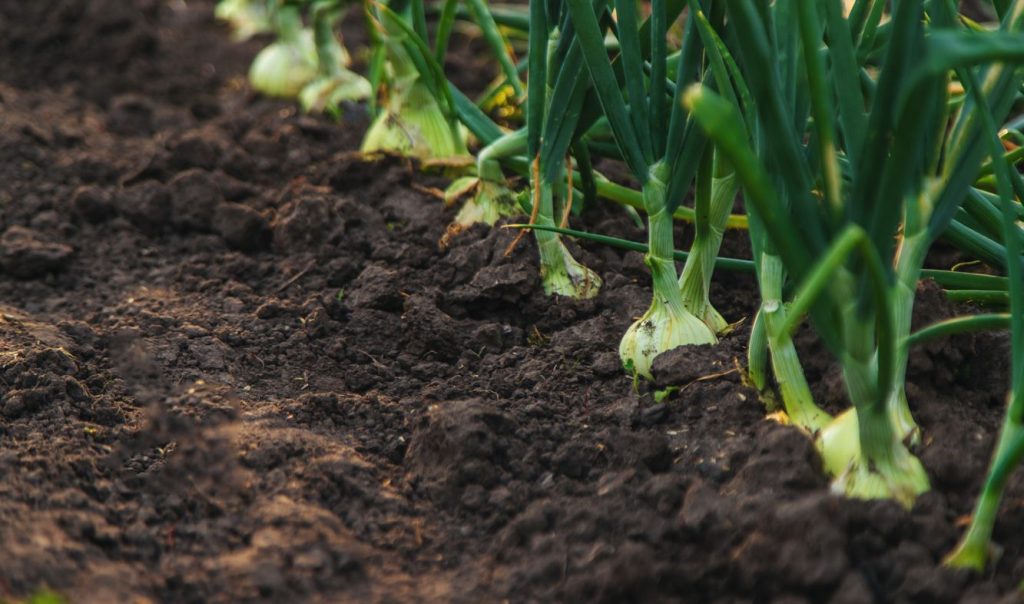

The foundation of any successful garden is healthy soil. Organic gardening relies on natural fertility, so focus on building nutrient-rich soil rather than depending on chemical fertilizers. Begin by testing your soil to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Incorporate organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold to improve soil structure, water retention, and fertility. Healthy soil encourages strong root systems and increases plant resistance to pests and diseases.
2. Choose the Right Plants
Selecting the right plants for your garden environment is crucial. Native and heirloom varieties are often more resilient to local pests and climate conditions, reducing the need for chemical interventions. Consider the sunlight, temperature, and moisture requirements of each plant, and group compatible plants together to optimize growth. Companion planting, such as growing basil alongside tomatoes, can naturally repel pests and enhance plant health.
3. Practice Crop Rotation
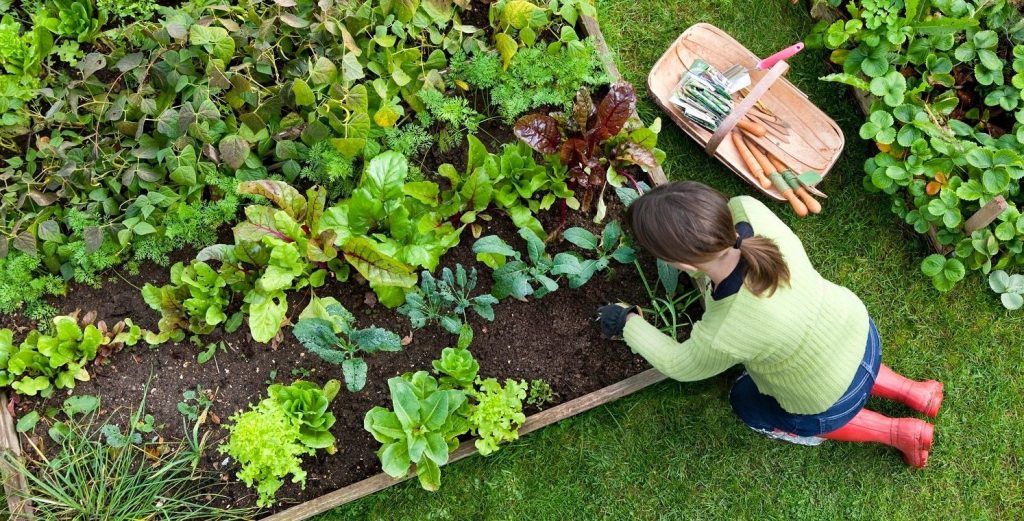

To prevent soil depletion and reduce the risk of disease, practice crop rotation. Avoid planting the same type of crop in the same spot year after year. Rotate families of plants—such as legumes, leafy greens, and root vegetables—to maintain soil fertility and disrupt pest and disease cycles. Crop rotation is a simple yet effective way to sustain long-term garden productivity.
4. Use Natural Fertilizers
Organic gardening avoids synthetic chemicals, so opt for natural fertilizers. Compost, worm castings, fish emulsion, and seaweed extract provide essential nutrients to plants without harming the environment. Apply fertilizers in moderation, as over-fertilizing can damage plants and disrupt soil balance. Mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips can also help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and gradually improve soil quality.
5. Implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Pest control in organic gardening relies on observation and prevention rather than chemicals. Use integrated pest management techniques to keep your garden healthy. Encourage beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory beetles that feed on harmful pests. Handpick pests when possible, and consider natural remedies like neem oil or insecticidal soap for severe infestations. Maintaining healthy plants and diverse ecosystems naturally reduces pest problems.
6. Conserve Water Efficiently
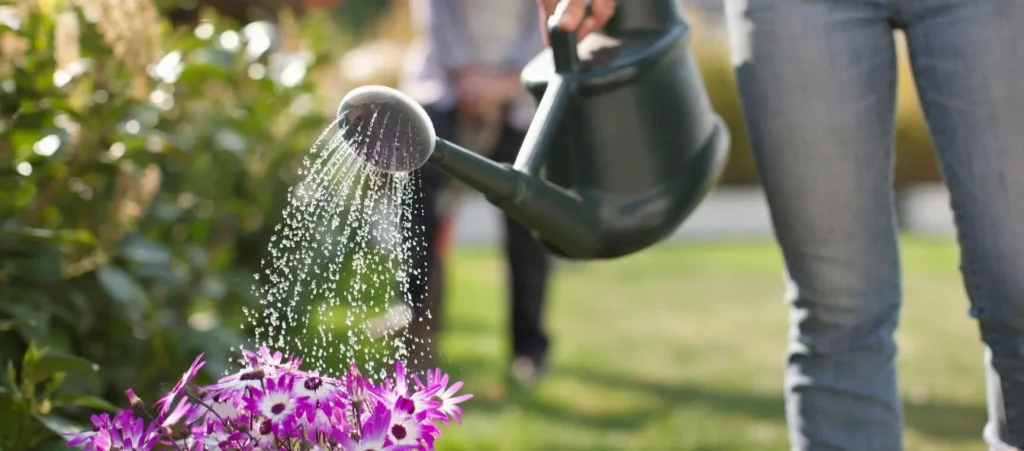

Water conservation is key to sustainable gardening. Water plants deeply but less frequently to encourage strong root development. Early morning or late evening watering reduces evaporation and prevents fungal diseases. Consider drip irrigation or soaker hoses for efficient water delivery. Collecting rainwater in barrels can also provide an eco-friendly water source for your garden.
7. Encourage Biodiversity
A thriving organic garden supports a diverse ecosystem. Plant flowers, herbs, and shrubs to attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Incorporate cover crops like clover or legumes to improve soil fertility and provide habitat for beneficial insects. A biodiverse garden not only supports plant health but also contributes to local environmental sustainability.
8. Practice Sustainable Weed Control
Weeds compete with garden plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. In organic gardening, focus on prevention and manual control. Mulching, hand-weeding, and using landscape fabrics are effective ways to manage weeds naturally. Avoid chemical herbicides, which can harm soil life and reduce biodiversity.
9. Maintain Garden Hygiene
Regular garden maintenance is essential for preventing disease and promoting plant growth. Remove diseased leaves, prune overgrown branches, and dispose of plant debris properly. Clean tools frequently to prevent the spread of pathogens. Good hygiene practices keep your garden healthy and reduce the need for intervention.
10. Be Patient and Observant
Organic gardening requires patience and attention. Observe your plants daily to detect early signs of stress, pests, or disease. Adjust watering, fertilization, and plant care as needed. Over time, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of your garden’s unique ecosystem, allowing you to make informed decisions that benefit both your plants and the environment.
Conclusion
Organic gardening is a rewarding way to grow food and flowers while protecting the planet. By focusing on soil health, choosing the right plants, practicing crop rotation, using natural fertilizers, and encouraging biodiversity, gardeners can create sustainable, thriving gardens. While organic gardening requires dedication, patience, and observation, the benefits—healthy plants, chemical-free produce, and a vibrant ecosystem—make it well worth the effort. Start small, stay consistent, and enjoy the satisfaction of cultivating a truly natural garden.