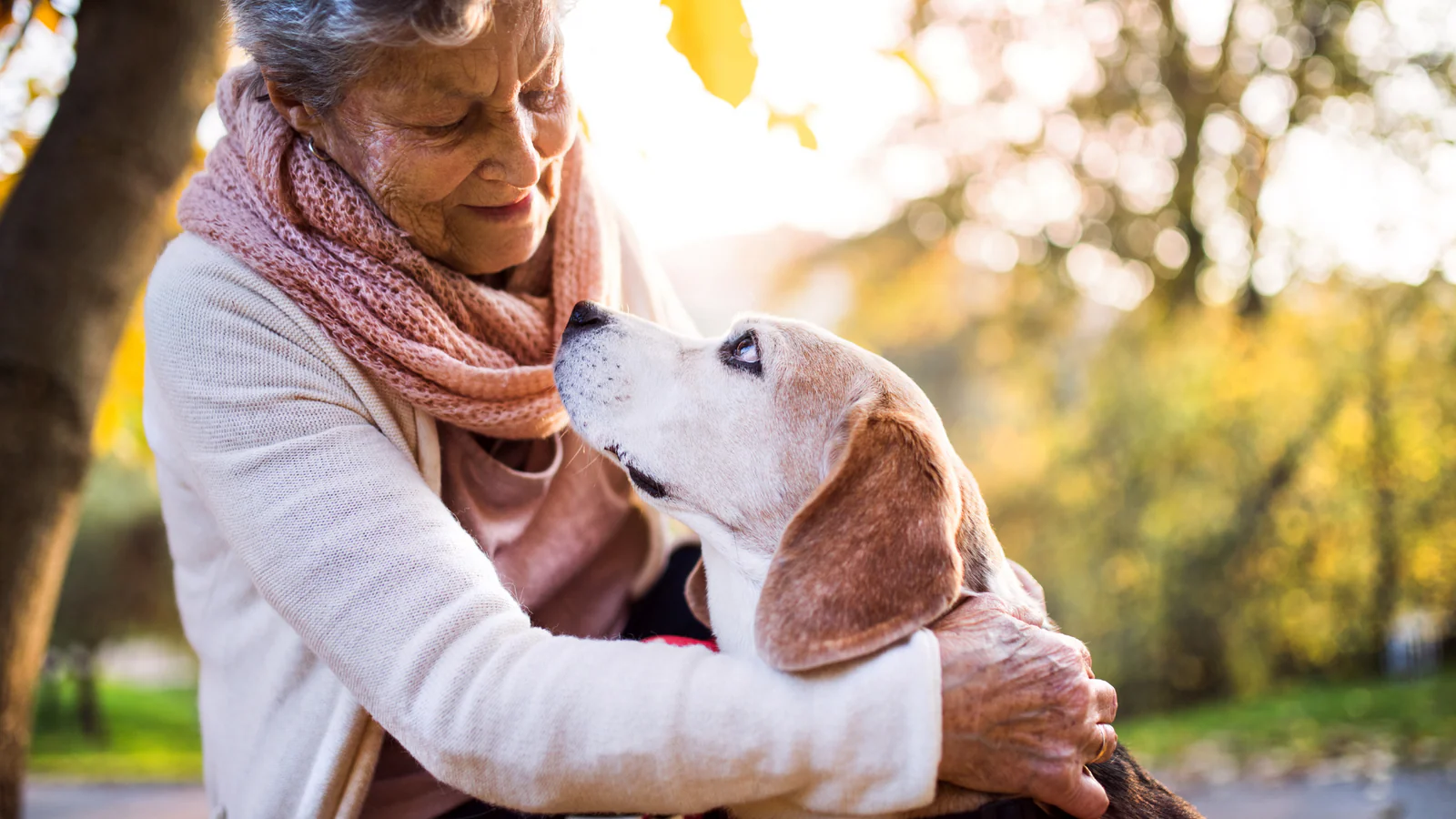
As pets age, their needs evolve, and taking care of senior pets requires extra attention, patience, and understanding. Just like humans, older pets can face health challenges, decreased mobility, and changes in behavior. With the right care, however, you can ensure your senior companion remains comfortable, happy, and healthy in their golden years. Here are essential tips for taking care of senior pets.
1. Regular Veterinary Checkups
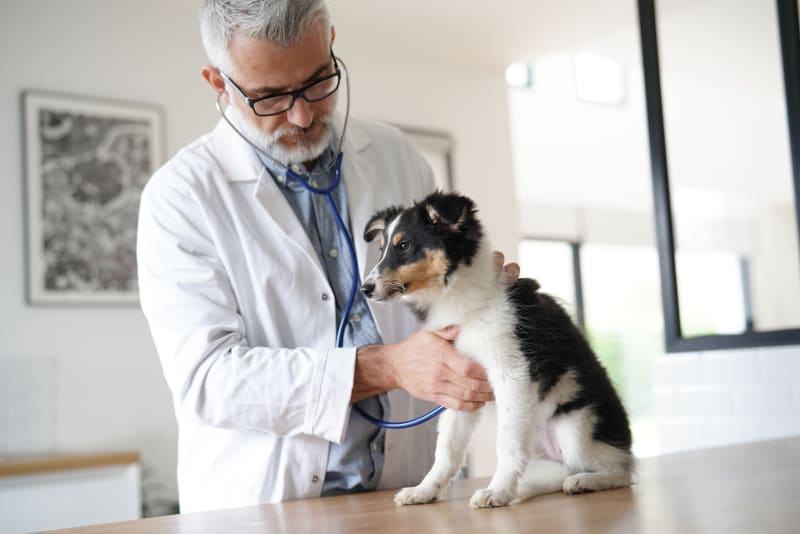

One of the most important aspects of senior pet care is frequent veterinary visits. Older pets are more prone to chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, kidney disease, and dental issues. Annual checkups may not be enough; many veterinarians recommend visiting every six months for pets over seven years of age. Routine exams help catch early signs of disease and allow for timely treatment, improving the pet’s quality of life.
2. Balanced and Age-Appropriate Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in the health of senior pets. As metabolism slows down, older pets may need fewer calories but more nutrients to support their immune system and maintain muscle mass. Look for senior-specific pet food that is rich in protein, low in fat, and contains essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Always consult your veterinarian before making changes to your pet’s diet, especially if they have medical conditions requiring specialized nutrition.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight

Weight management is crucial for senior pets. Excess weight can worsen joint problems, diabetes, and heart disease, while being underweight can signal underlying health issues. Monitor your pet’s body condition regularly and adjust their diet and exercise routine accordingly. Gentle, regular exercise, such as short walks for dogs or interactive play for cats, helps maintain mobility and overall health.
4. Dental Care
Dental health is often overlooked, yet it is essential for senior pets. Tooth decay, gum disease, and oral infections can lead to pain, difficulty eating, and systemic health problems affecting the heart, liver, and kidneys. Regular brushing, dental chews, and professional cleanings as recommended by your veterinarian can prevent these issues.
5. Monitor Behavior and Mental Health
Aging can affect a pet’s cognitive abilities. Senior pets may develop anxiety, confusion, or changes in sleep patterns. Keep an eye out for signs of cognitive dysfunction, such as disorientation, excessive vocalization, or forgetting trained behaviors. Mental stimulation through interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and gentle training exercises can help maintain cognitive function and prevent boredom.
6. Joint Health and Comfort
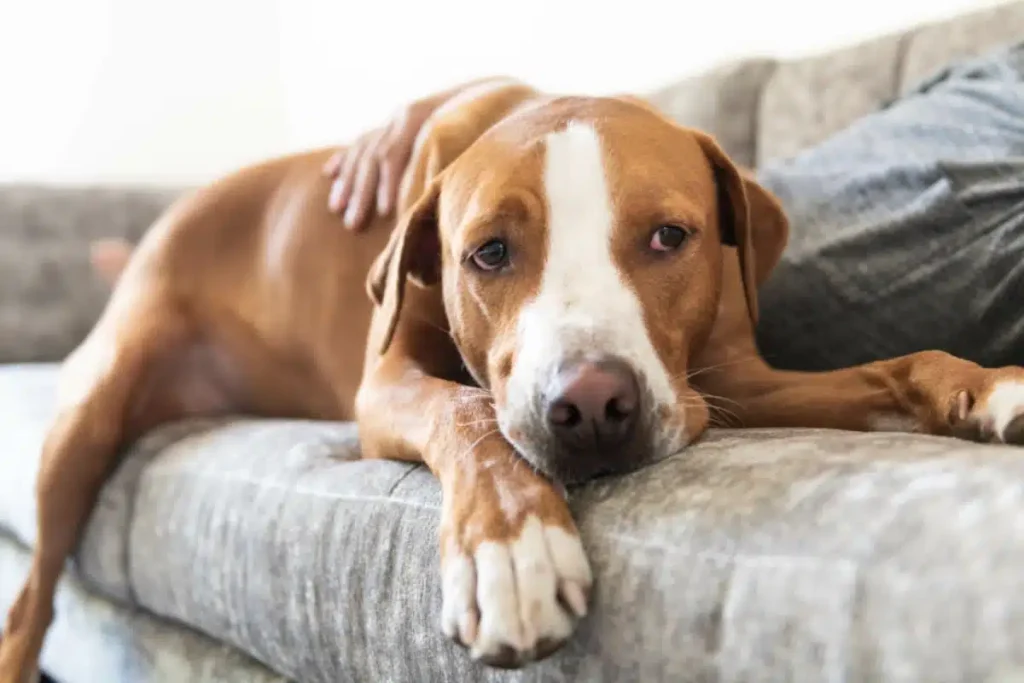

Arthritis and joint stiffness are common in older pets. Providing orthopedic beds, ramps, or steps for easy access to favorite spots, and avoiding slippery floors can prevent injuries and ease discomfort. Your veterinarian may recommend supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin or prescribe medications to manage pain and inflammation. Regular low-impact exercise keeps joints flexible and muscles strong, improving mobility and overall well-being.
7. Grooming and Skin Care
Senior pets may have more fragile skin and thinning fur. Regular grooming helps prevent mats, reduces shedding, and allows you to check for lumps, skin infections, or parasites. Keep their coat clean and trimmed, and pay attention to signs of skin irritation or infections. Bathing should be gentle and infrequent unless recommended by your veterinarian.
8. Monitor Elimination and Hydration
Changes in urination or bowel movements can indicate health problems in older pets. Ensure your pet has easy access to water and litter boxes or outdoor areas. Dehydration can be a concern, especially in older cats and dogs with kidney issues. Encourage drinking by providing fresh water, using water fountains, or offering wet food for cats.
9. Maintain a Routine
Senior pets thrive on consistency. Keep feeding, walking, and bedtime routines predictable to reduce stress. Sudden changes in environment, schedule, or household members can confuse older pets, especially those with cognitive decline.
10. Provide Love and Attention
Finally, senior pets need emotional care just as much as physical care. Spending quality time, giving gentle affection, and creating a calm, comforting environment improves their happiness and quality of life.
Conclusion
Caring for a senior pet requires vigilance, compassion, and proactive health management. By providing proper nutrition, regular veterinary care, comfortable living conditions, and emotional support, you can help your aging companion enjoy their later years with dignity and joy. Senior pets may move slower and require more patience, but their loyalty and love remain as strong as ever. With these tips, you can ensure your cherished companion ages gracefully and happily.